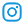
A Dual DC Power Supply, also known as a dual-output DC power supply, refers to a power supply device that integrates two independent adjustable DC power supply outputs into one chassis.
Detailed Introduction with Application Fields
Combining the characteristics of a dual dc power supply and the parameters of this multi-specification power supply board (7.5V/2.4A, 9V/2A, 12V/1.5A, 18W per channel), below is a comprehensive introduction covering core details and specified application fields, optimized for foreign trade websites.
Core Attributes of the Power Supply Board & Adaptation Logic with Dual DC Power Supply
1. Basic Parameters & Performance Positioning
Output Specifications: Three sets of fixed DC outputs (7.5V/2.4A, 9V/2A, 12V/1.5A), each with 18W power (Voltage × Current). Supports single-channel independent output or dual-channel combined output (requires the power board to support series/parallel functions).
Core Advantages: Integrates the "independent power supply" feature of dual DC power supplies with the "adaptability flexibility" of multi-specification outputs. Eliminates the need for additional Power Adapters, simplifying wiring and power supply logic.
2. Functional Linkage with Dual DC Power Supply
Independent Mode: Dual channels can select different specifications separately. For example, one channel powers a fixed-voltage device, and the other powers another type of device, with no mutual interference.
Series Mode (if supported): Connect the positive pole of one channel to the negative pole of the other (e.g., 7.5V positive to 12V negative). The total voltage equals the sum of the two channels (19.5V), and the total current is limited by the smaller value (1.5A), suitable for devices requiring special voltages.
Parallel Mode (if supported): Connect the positive and negative poles of two same-specification outputs (e.g., two 9V/2A channels). The total voltage remains unchanged (9V), and the total current is the sum of the two channels (4A), with power increased to 36W, suitable for high-current-demand devices.
Detailed Adaptation Schemes for Key Application Fields
1. Low-Voltage Distribution Box
Core Adaptation Requirements: Low-voltage distribution boxes need centralized power supply for optical modems, POE switches, mini NVRs, etc., requiring stable voltage and neat wiring.
Optical Modem: Most models are compatible with 9V/2A. Power via single-channel independent output to avoid power competition affecting signal stability.
Small POE Switch: Some low-power POE switches support 12V/1.5A. In dual-channel mode, it can power both the switch and optical modem simultaneously, reducing the number of power adapters in the box.
Mini NVR: Compatible with 12V/1.5A. If connecting surveillance cameras (12V) at the same time, enable parallel mode (two 12V/1.5A channels) to provide a total current of 3A, meeting the power needs of the NVR + cameras.
Advantages: Centralized power supply reduces cable clutter. Dual-channel isolation design avoids electromagnetic interference between devices, enhancing the stability of the low-voltage system.
2. Routers & Switches
Core Adaptation Requirements: These network devices require high voltage stability, with rated voltages mostly 9V or 12V and current demands of 1-2A.
Home Routers: Mainstream models (e.g., some ASUS, Xiaomi models) are compatible with 9V/2A. Single-channel power supply meets daily use. In dual-channel mode, it can power the main router + mesh router simultaneously.
Gigabit Switches (8 ports or less): Most low-power switches support 12V/1.5A or 9V/2A. If the switch and router are in the same distribution box, dual-channel independent output can power them separately, avoiding total network outage due to single power failure.
Advantages: 18W single-channel power provides sufficient redundancy. Overcurrent protection prevents device damage from short circuits. Dual-channel design supports backup power supply for network devices.
3. 3C Products
Core Adaptation Requirements: Covers mobile phones, tablets, portable speakers, external hard disk enclosures, etc., with diverse voltage specifications requiring flexible adaptation.
2.5-inch External Hard Disk Enclosures: Generally compatible with 12V/1.5A or 9V/2A. Single-channel power supply meets the power needs of hard disks during high-speed reading/writing, avoiding data transmission interruptions due to insufficient voltage.
Portable Bluetooth Speakers: Most small speakers are compatible with 7.5V/2.4A or 9V/2A. Single-channel power supply works for outdoor use. In dual-channel mode, it can charge the speaker and mobile phone (with a step-down cable) simultaneously.
Older Android Tablets: Some models support 9V/2A charging. This power board provides more stable power than ordinary Chargers, suitable for long-term plug-in use (e.g., car navigation, home central control screens).
Advantages: Multi-specification coverage meets the needs of most 3C products. Dual-channel combined mode supports "device use + charging" simultaneously, expanding applicable scenarios.
4. Other Extended Applications
Electronic Experiments/DIY Projects: Students or electronics enthusiasts can use dual-channel independent output to power analog circuits (7.5V) and digital circuits (12V) separately for easy debugging and comparison. Series mode can simulate special voltage signals, enhancing experimental flexibility.
Small LED Devices: Such as 12V LED strips and 7.5V desktop LED lamps. Single-channel 12V/1.5A can drive 12V LED strips within 5 meters. Dual-channel parallel mode can extend to 10 meters, meeting home lighting or decoration needs.
Usage Notes (Ensuring Safety & Stability)
Precise Voltage Matching: All devices must use the corresponding output specification. Never connect 12V output to a 9V device (which will burn the motherboard); conversely, low-voltage input to a high-voltage device will cause it to fail to work.
Power & Current Limitations: Single-channel output power must not exceed 18W. Total power after dual-channel combination must not exceed the power board’s rated total power (usually 36W, subject to product labeling). The device’s rated current must not exceed the maximum current of the corresponding output.
Mode Usage Specifications: Series/parallel modes are only applicable to the same type of devices, and the power board must support these functions. Do not arbitrarily connect different specification outputs in series to avoid voltage conflicts.
Interface & Protection: Use matching DC connectors (e.g., mainstream 5.5mm×2.1mm specification) to avoid overheating caused by poor contact. Rely on the power board’s overvoltage, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection functions; do not modify the output interface by yourself.
Summary
This multi-specification power supply board integrates the independent power supply feature of dual DC power supplies with the advantage of multi-voltage output, offering strong adaptability in low-voltage distribution boxes, network devices, 3C products, and other fields. Its core value lies in "centralized power supply + flexible combination"—it reduces the number of power adapters while improving power supply stability through dual-channel isolation and power redundancy design. It is particularly suitable for scenarios requiring neat wiring and reliable device performance.